Apart from reducing transaction costs, one of the significant advantages of rupee invoicing in foreign trade is the increased price transparency and faster settlement times.
The concept of rupee invoicing gained prominence after the RBI circular in July 2022, which allowed trade transactions (exports/imports) to be conducted and settled in Indian rupees.
Under the new Foreign Trade Policy (FTP) 2023, there is a strong emphasis on promoting exports through rupee invoicing. The policy proposes that both trading partners should raise their invoices and settle payments for transactions in rupees on a bilateral basis. This framework facilitates invoicing of both exports and imports in rupees, establishes market-determined exchange rates between currency pairs of the trading partners, and enables trade settlement through the use of a Special Rupee Vostro Account (SRVA).
According to the BIS Triennial Central Bank Survey 2022, the US dollar dominated the global forex turnover, accounting for 88 per cent of daily averages in 2022. It was followed by the Euro (31 per cent), Japanese Yen (17 per cent), and Pound Sterling (13 per cent). In contrast, the Indian rupee constituted only 2 per cent of the global currency market turnover.
Similarly, based on the IMF's COFER data for 2022 Q4, the US dollar held the largest share of global foreign exchange reserves at 58.4 per cent. The Euro accounted for 20.5 per cent, the Japanese Yen 5.5 per cent, the Pound Sterling 5 per cent, the Chinese Renminbi 2.7 per cent, the Canadian dollar 2.4 per cent, the Australian dollar 2 per cent, and the Swiss Franc 0.2 per cent. India's share in global foreign exchange reserves was negligible.
The advantages of using rupee invoicing are significant, particularly during times of geopolitical unrest and economic sanctions imposed on India's major trade partners.
The advantages of rupee invoicing encompass various aspects, including the reduction of transaction costs, enhanced price transparency, quicker settlement times, facilitation of international trade, decreased hedging expenses, lower RBI foreign reserve holding costs, and crucially, the internationalization of the Indian rupee.
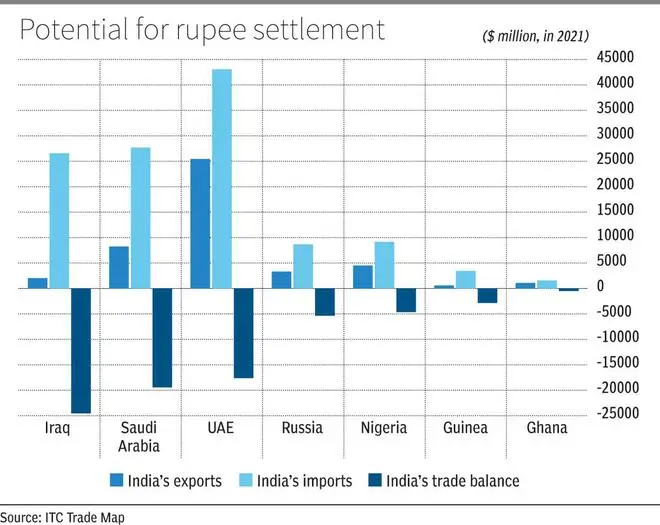
Research indicates that opting for invoicing in rupee would prove advantageous in trade partnerships with countries like Russia, Saudi Arabia, Nigeria, and the UAE, where India plays a significant role as an importer, while also having potential for Indian exports.
The Chart illustrates some of the countries that offer potential for trade settlement in rupee.
India's efforts to promote trade in rupees have been steadily gaining traction, as evident from the significant increase in the number of Special Rupee Vostro Accounts (SRVAs), which rose to 60 within just seven months (as mentioned in a Rajya Sabha question on March 14). Currently, eighteen countries have established SRVAs to facilitate overseas trade using the Indian rupee. However, it is noteworthy that out of these countries, India experienced a trade deficit with eight nations in FY22, namely Botswana, Germany, Guyana, Malaysia, Myanmar, Oman, Russia, and Singapore.
The effectiveness of rupee trade, in the end, relies on two key factors: firstly, whether India maintains a net trade deficit or surplus with the trading partners participating in this mechanism, and secondly, the proportion of trade conducted in rupees in comparison to the overall bilateral trade volume.





.jpg)
